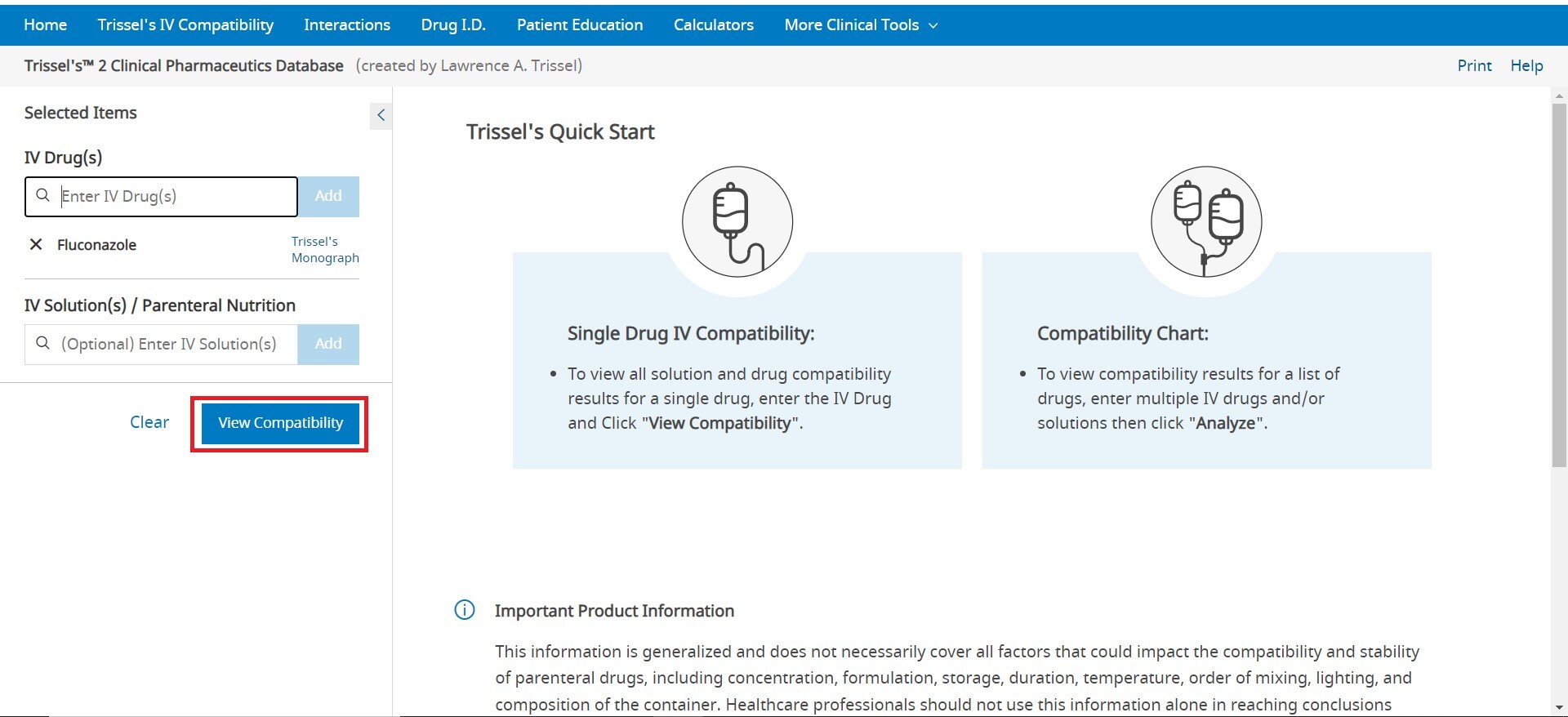
The Interactions tool is accessed via the blue tool bar at the top of the screen. This drug and herbal interaction analysis tool is designed to identify potential drug-drug interactions, drug-allergy interactions, and duplicate therapy interactions. Begin by entering the list of medications and known drug allergies to be analyzed. The interactions tool allows users to enter medications (both prescription and over-the-counter), natural products, foods and/or alcohol.
Allergies may be entered by medication name (e.g., aspirin) or by the pharmacologic class (e.g., salicylates).
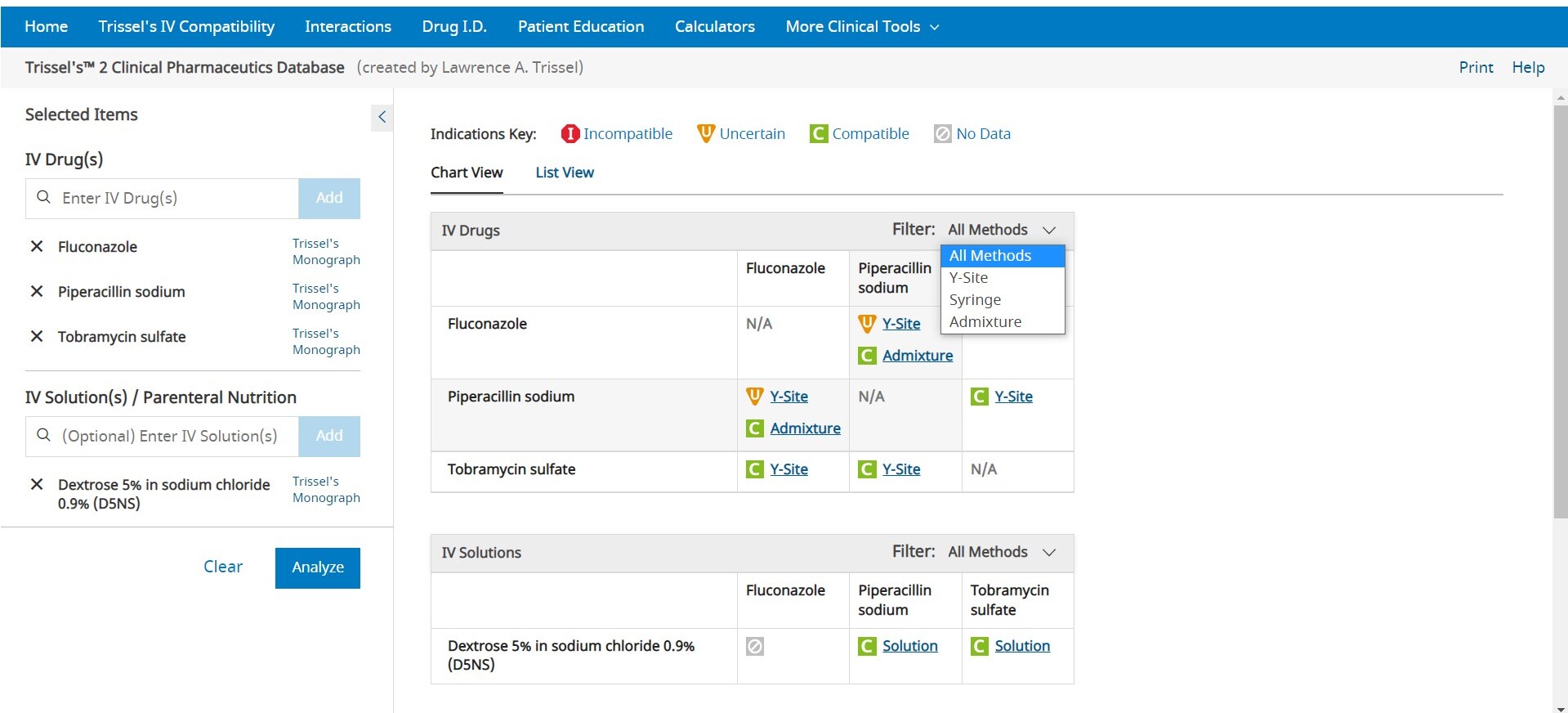
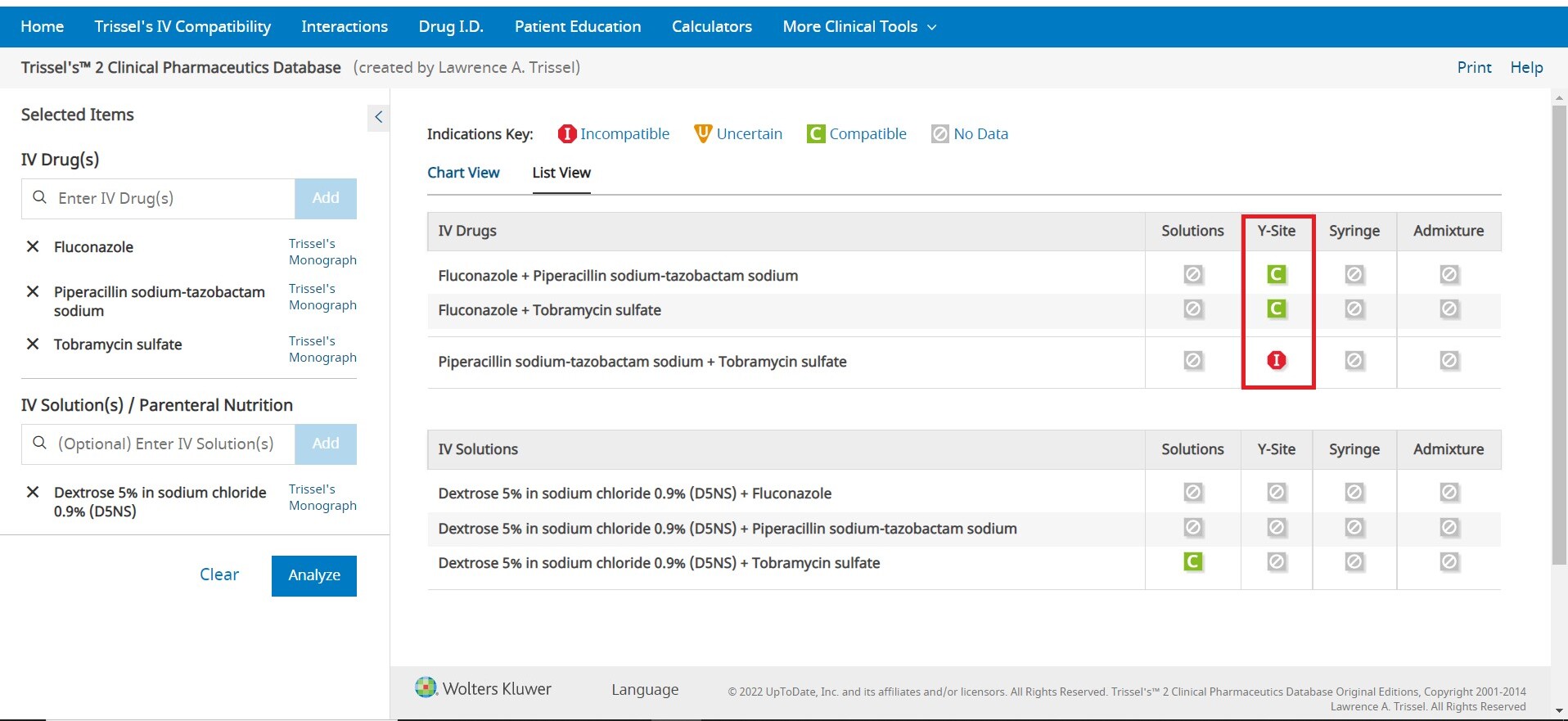
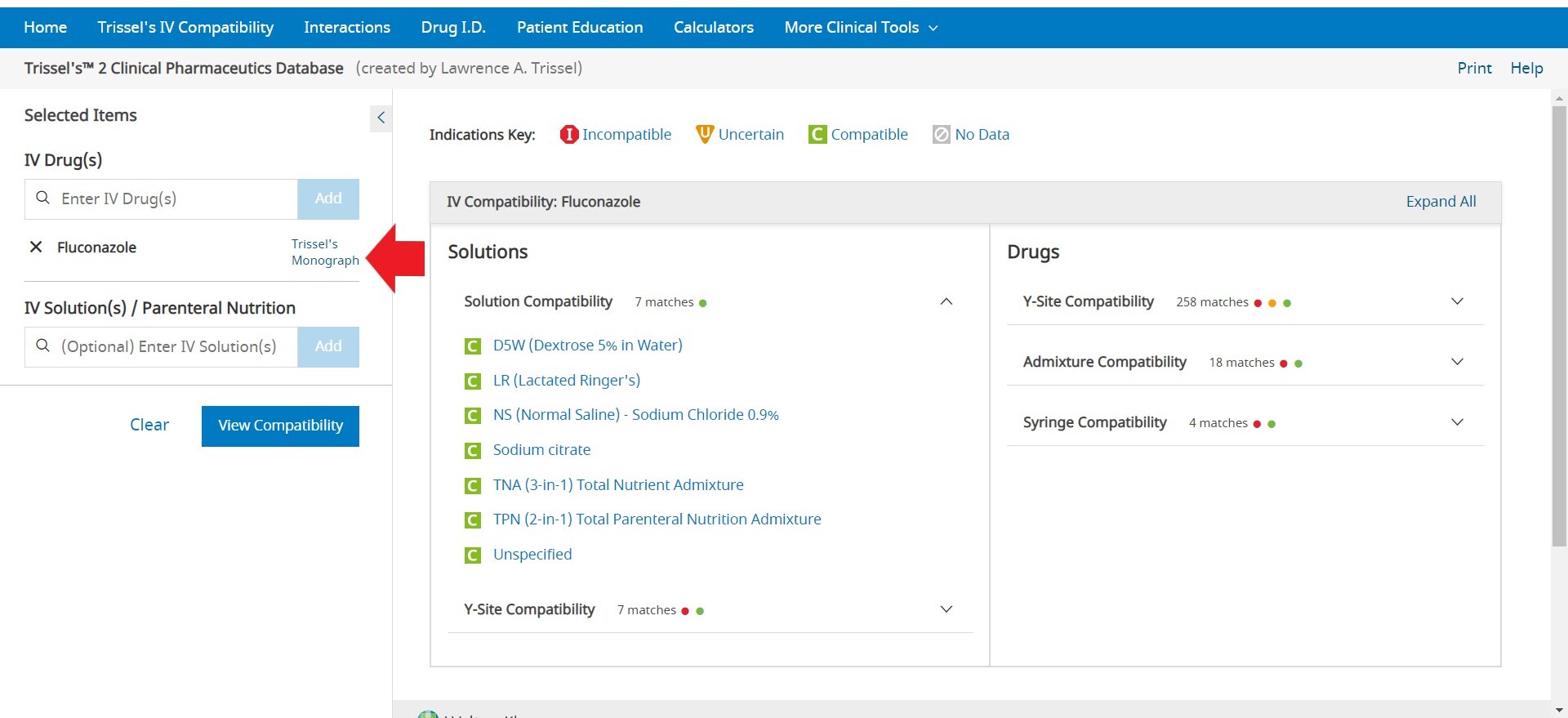
To enter an item, begin typing a keyword into the “Drugs” and/or “Allergies” box in the left pane. After you enter at least two (2) characters, suggested terms will populate, and you can select the desired term from the list. Continue this process until all items are added. To remove an item from the list, uncheck the selected box next to the product you wish to remove. Once the list is complete, click the Analyze button to perform an analysis. If you are looking to see all interactions for a single drug, click on Single Drug Analysis next to the name of any drug that has been added to the drug list. If only a single drug is entered, click View Interactions to see the list of all interactions for the single drug.
The Duplicate Drug Therapy feature is automatically checked to provide information about selected medications that are considered duplicate therapies because they belong to the same pharmacologic class. If you do not want the duplicate therapy screening to be performed, the box can be unchecked prior to selecting the Analyze button.
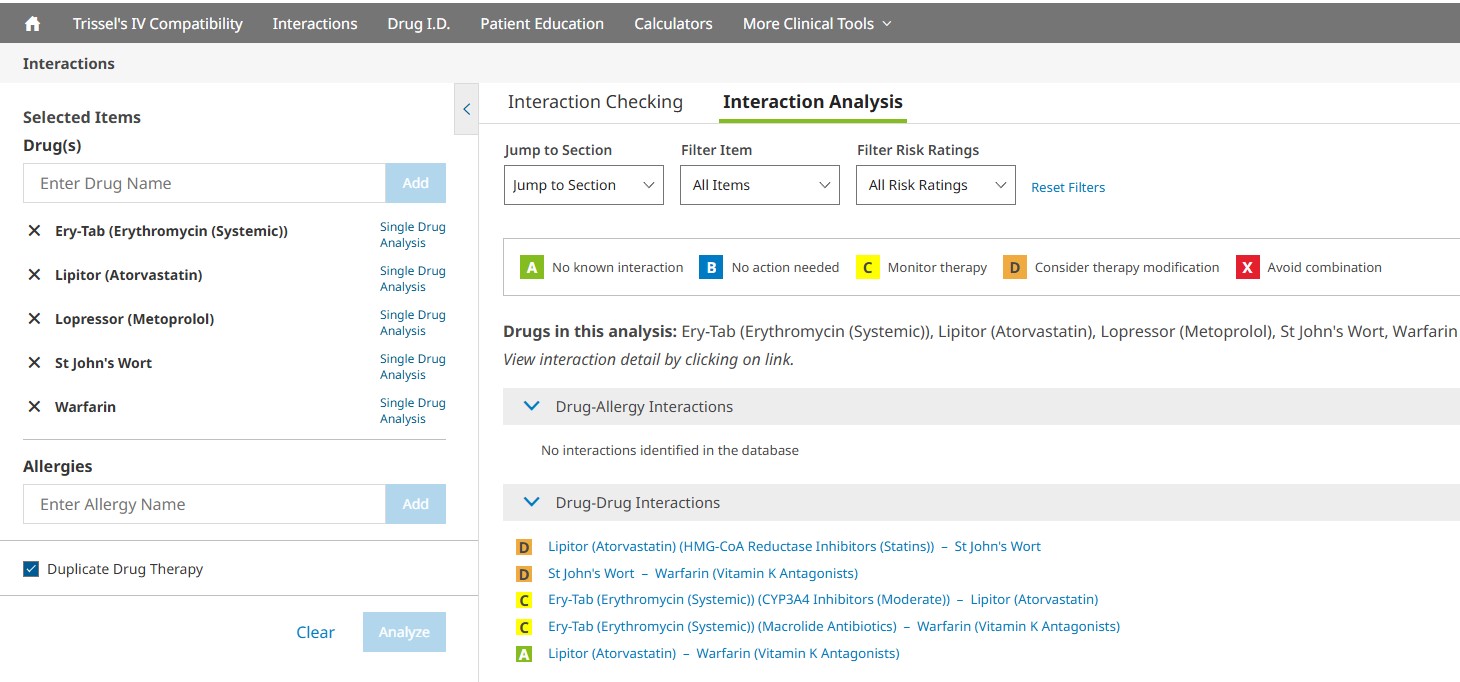
The Interaction Analysis screen provides a summary of interactions organized by drug-drug, drug-allergy, and duplicate therapy sections. The summary statements include the search terms used, along with the corresponding generic name(s), if applicable. An assigned risk rating (A, B, C, D or X) appears next to each drug-drug and drug-allergy interaction. Each letter represents a different level of urgency in responding to the identified interactions.
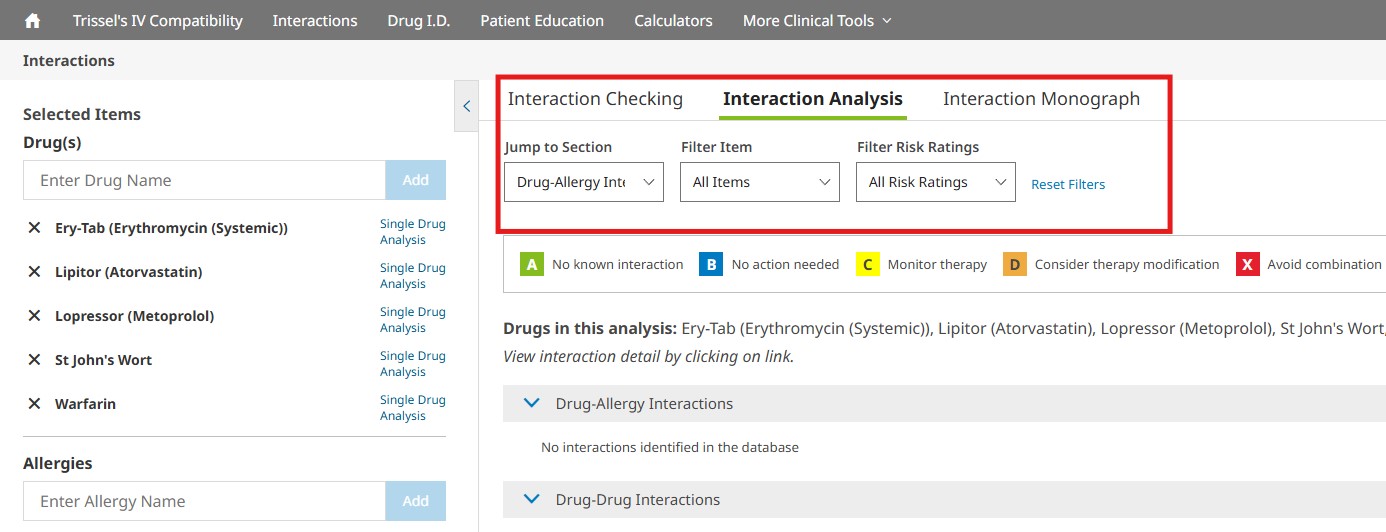
You can jump to a particular screening category or filter the interactions that are displayed on the Interaction Analysis screen by using the available drop- down menus. You may filter by drugs or allergies entered and/or by various risk ratings. To remove the filters selected, simply click the Reset Filters button to return to the full, unfiltered interaction analysis results. In addition to the risk rating scale, dependencies associated with a particular drug interaction will also be listed. The risk ratings and dependencies are defined in more detail below.
Dependencies and risk rating scale
Dependencies (if applicable): Identifies various factors that may influence the occurrence or severity of the interaction. The factors may involve patient-specific variables, such as organ dysfunction (e.g., renal/hepatic), smoking status, genotype (e.g., VKORC1 haplotype), or phenotype (e.g., CYP2D6 poor metabolizer). Additional factors may relate to specific pharmaceutical dosage forms, routes of administration and/or specific dosing regimens. The presence of one or more factors may result in an increased risk and/or severity of interaction, or conversely, disqualify an interaction. Highlighting this information at the top of the monograph helps the clinician evaluate the interaction relevance for a specific patient.
Risk Rating: Provides an indicator to help a clinician quickly decide how to respond to the interaction data. Each drug-drug interaction is assigned a risk rating of A, B, C, D, or X. The progression from A to X shows, as a general matter, an increasing urgency associated with the data. In general, A and B monographs are of more academic than clinical concern. Monographs rated C, D, or X indicate situations that will likely demand a clinician’s attention. The text of the “Patient Management” section of the monographs will provide assistance regarding responses that may be generally useful for many patients. Each drug-allergy interaction is assigned a risk rating of X. The definition of each risk rating is as follows:
| Risk rating |
Action |
Description |
| A |
No known interaction |
Data have not demonstrated either pharmacodynamic or pharmacokinetic interactions between the specified agents. |
| B |
No action needed |
Data demonstrate that the specified agents may interact with each other, but there is little to no evidence of clinical concern resulting from their concomitant use. |
| C |
Monitor therapy |
Data demonstrate that the specified agents may interact with each other in a clinically significant manner. The benefits of concomitant use of these two medications usually outweigh the risks. An appropriate monitoring plan should be implemented to identify potential negative effects. Dosage adjustments of one or both agents may be needed in a minority of patients. |
| D |
Consider therapy modification |
Data demonstrate that the two medications may interact with each other in a clinically significant manner. A patient-specific assessment must be conducted to determine whether the benefits of concomitant therapy outweigh the risks. Specific actions must be taken in order to realize the benefits and/or minimize the toxicity resulting from concomitant use of the agents. These actions may include aggressive monitoring, empiric dosage changes, or choosing alternative agents. |
| X |
Avoid combination |
Data demonstrate that the specified agents may interact with each other in a clinically significant manner. The risks associated with concomitant use of these agents usually outweigh the benefits. Concurrent use of these agents should generally be avoided. |
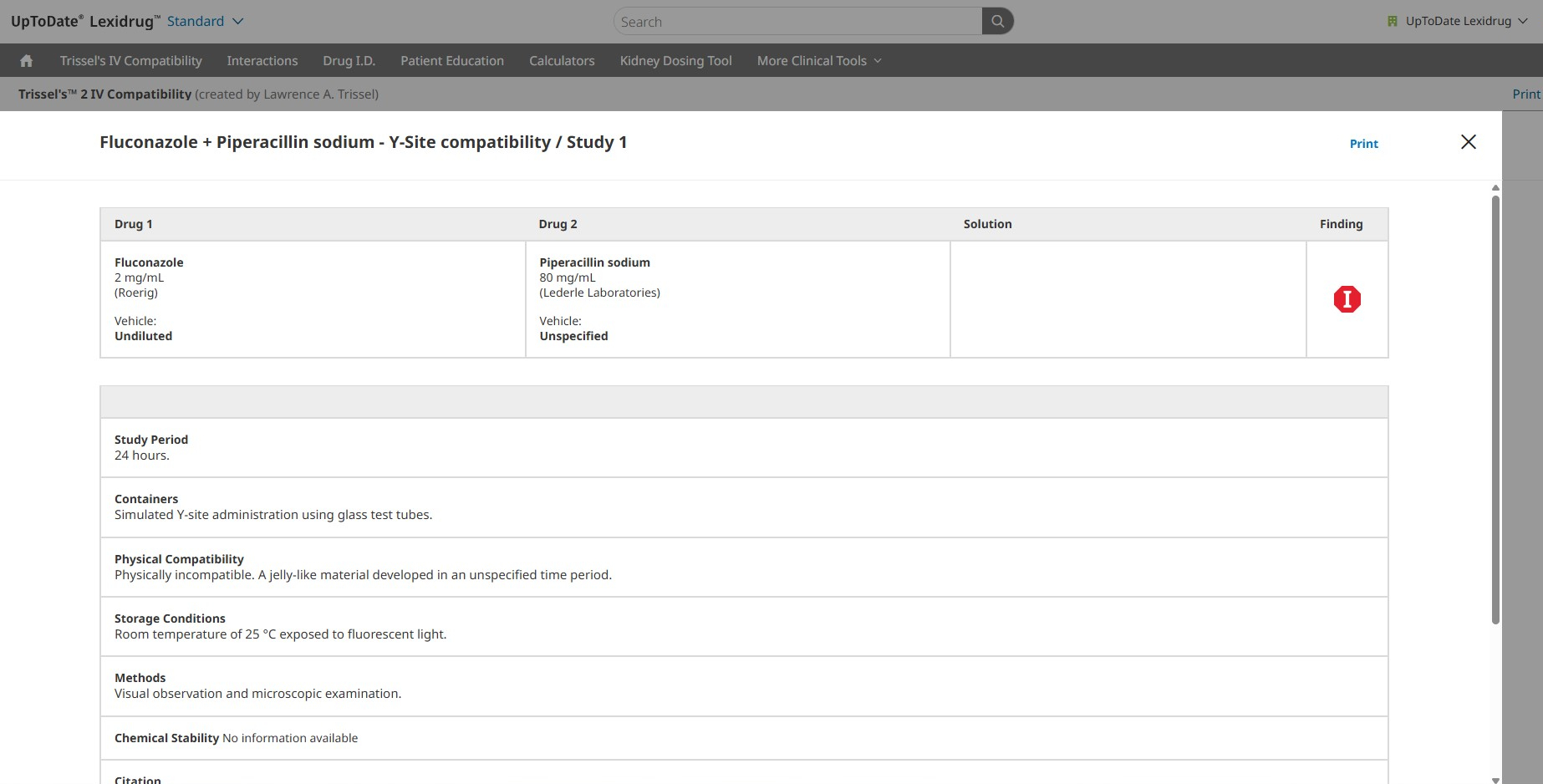
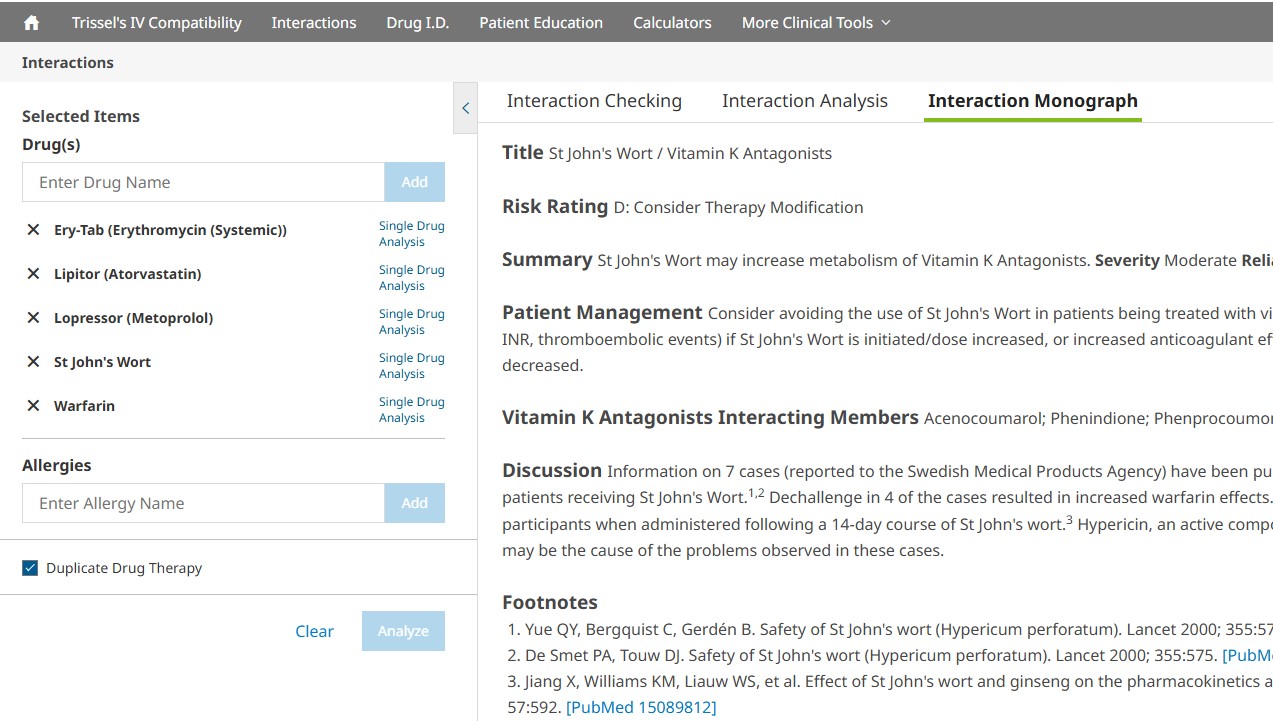
Click on the interaction link to review the Interaction Monograph. This monograph will provide detailed information, including:
- Interacting members, class exceptions
- Patient management
- Fully referenced discussion of the available literature
- References (including PubMed links when appropriate)
Click on the hyperlinked allergy link to review the allergy monograph. This monograph will provide detailed information, including:
- Reactions reported as well as other relevant information for the clinician
- Fully referenced discussion of the available literature
- References (including PubMed links when appropriate)
To return to the Interaction Analysis summary page, click on the “Interaction Analysis” tab at the top of the content panel. To return to the initial search screen to enter an additional item, click on the “Drugs” tab at the top of the content panel.
The Clear button will clear all items from the list and allow the user to start a new regimen.